Not only are the following factors important, but combined, they are hugely important. It’s possible not every factor will apply to your site, but the vast majority will have a big influence your rankings and visibility.
Contents:
- Layout & Design
- Use of Relevant Keywords, Phrases, & Topics
- Use of Optimized Images and Video
- Personalization
- Authority + Trust of Links
- Relevance of Links
- Social Sharing
- Page Structure
- Content Depth
- Topical Authority
- Structured Data
- Hreflang for Internationalization
- Volume of Brand Searches
- AMP
- HTTPS
1. Layout & Design
Appearance matters. So does page layout.
In SEO, everything is connected.
Not only is page layout a confirmed Google Ranking Factor in more ways than one (aggressive ads and page segmentation, to name a few) but having a clean, modern design with clear navigation and site elements can lead to:
- Better engagement
- More shares + links
- Increased conversions
How to Leverage
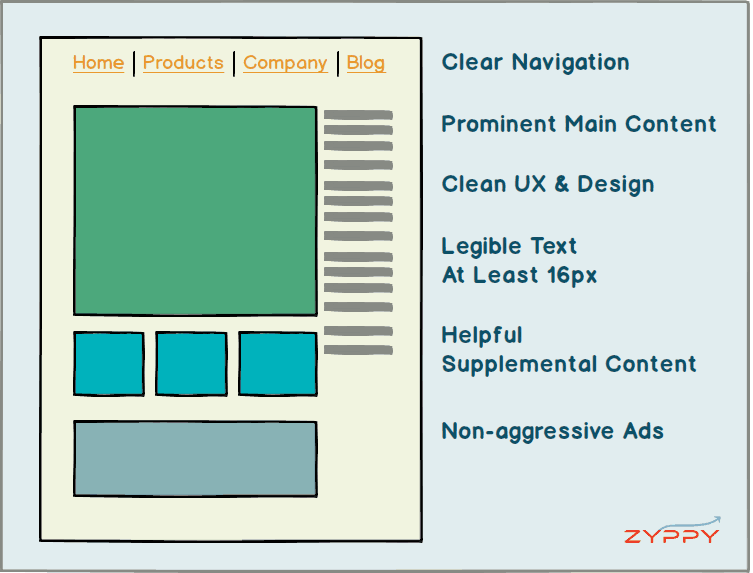
While there no single “right” way to design and organize a page, a handful of guidelines go a long way in helping to get your message across, and to rank.
- Clear navigation
- Prominent main content – typically above the fold
- Helpful supplemental content
- Clean UX and design
- Non-aggressive ads
- Legible Text (at least 16px)
2. Use of Relevant Keywords, Phrases, & Topics
Well, duh.
If you want to target users who search using specific words and phrases, it’s 100% helpful to include those phrases and topics in key sections of your site.
In the early days, “keyword stuffing” might have been your entire SEO strategy. Today, the importance of individual keywords has fallen dramatically while Google has gotten amazingly better at figuring out the meaning of your content, including synonyms, variations, topics, entities, and intent.
Keyword stuffing is out, but it’s still helpful to include phrases, synonyms, and topics that your audience is looking for in key places. These areas include:
- The page title
- Meta descriptions
- URL
- Domain name (sometimes)
- Page headings
- Body text
- Image alt attributes (when appropriate)
- Metadata
How to Leverage
- Use on-page SEO best practices to target your content towards specific phrases and topics:
- Move beyond keyword to optimize for complete topics and entities:
3. Use of Optimized Images and Video
It’s totally possible to rank in Google without using images or videos.
That said, sites that use different forms of visual media, on average, typically outrank sites that don’t.
Images and media can make content more engaging and shareable, and the data they add through optimization can be used by search engines to help with rankings for relevant terms.
How to Leverage
Aside from adding original and unique images and video in your text, it’s important to ensure the media both ads to the user experience, as well as follows basic optimization guidelines. Here are a couple of guides covering both video and image SEO:
- Wistia’s Guide to Video SEO
- Image SEO: Optimize images for search engines
- Image SEO: The Ultimate Guide
4. Personalization
In 2009, Google turned on personalized search for everyone.
If you visit a site, and Google thinks you had a good experience, they are more likely to surface that site again in your search results.
Other factors that influence personalization include:
- Location
- Mobile App use
- Email history
- Shopping history
- Maps history
- Device
- … and many more (rumored to be over 2000+ signals)
The basics of personalization are two-fold:
- The more a user interacts with your website + brand, the more likely Google may surface you in the users search results
- The more relevant you are to a user’s immediate need (i.e., location + intent), the more likely for Google to connect you
How to Leverage
For websites, increasing engagement through all available channels is the key to increasing visibility through personalized search. This means positively engaging your visitors/customers through all points of possible contact including your website, emails, app installs, and even your physical location, when applicable.
To put it simply: make sure they want to engage with you again!
For a business with physical locations, local intent is a huge factor in personalized search. Make sure your Local SEO is dialed in as tight as possible.
5. Authority + Trust of Links
Authority and trust are subsets of link quality.
Link Authority may encompass many things. While we don’t know all the ingredients in Google’s secret sauce, Link Authority is mostly thought of as the raw power all the links pointing to a page.
The more high-quality links a page has pointed to it, the more authority it has to pass to other pages through links. For example, Wikipedia has significantly more link authority than a typical personal blog.
Link Authority is often referred to as PageRank.
Trust is another aspect of authority worth considering. A spam website may have a ton of links pointing at it (through manipulation), but because Google wants to factor out spam, it can take the trust of the website into consideration.
It may do this by starting with a set of trusted seed sites (government, universities, newspapers, etc.) and measuring the number of link “hops” between sites. Sites further away from trusted sites are more likely not to be trusted.
How to Leverage
Many types of links are valuable, but generally, you want to seek links from trusted, high authority sites.
Many SEO tool providers offer link metrics. Both Moz and Majestic offer link metrics (although limited at the free level)
- Majestic: Important metrics are Trust Flow and Citation Flow
- Moz Link Explorer: Important metrics are Domain Authority and Spam Score
6. Relevance of Links
Imagine you own a pizza shop in Honolulu. If you were Google, which of the following would you give more weight?
- A German plastic manufacturer links to you with the word “website”
- A Hawaiian restaurant critic links to you with the words “best pizza in Hawaii”
Hopefully, you chose the latter. Google would too.
Link Relevance may be influenced by many things, among them:
- Anchor Text
- The relevance of the linking page (through means such as phrase-based indexing)
- Local interconnectivity, i.e., links from pages that rank well for your term can help you to rank
How to Leverage
By researching your link targets properly, work to secure links that are relevant to your topics.
Remember the Golden Rule of Link Building: Will this link bring engaged, highly qualified visitors to my website?
Read: 7 Illustrations of How Topical Links Impact Rankings
7. Social Sharing
If you want to watch SEOs argue, bring up social sharing as a ranking factor.
But we’re not going to argue today because this isn’t about ranking factors. This is about success factors.
On one hand, Google has consistently stated they don’t use raw social counts in their ranking algorithms. On the other hand, studies shows a strong correlation between social sharing and higher rankings.
It doesn’t matter how it works. It’s widely agreed that broad social sharing can help a page to rank, either directly or—more likely–indirectly.
The reason is simple: regardless of algorithms, social sharing can put your content in front of more eyeballs. Marketing 101. Content with wide social sharing enjoys greater distribution in front of influencers, and social sharing aggregators can often create downstream links to the page.
How to Leverage
No magic bullets here. They key is to build your social influence and create content that encourages social sharing. It’s not a strategy everyone can master, but it’s powerful.
8. Page Structure
Similar to Layout and Design, Page Structure helps you to organize your content in ways that Google can better understand it and display in search results.
How to Leverage
Best practices for Page Structure include:
- Organize your content into clear hierarchy of titles, headings (h1, h2, h3, etc.), body text, lists and tables
- Use subheadings when called for
- Group thematically related ideas together, i.e., within the same content blog, paragraph, list, etc
- Use an Inverted Pyramid style of writing
- Optimize further for Featured Snippets
9. Content Depth
Consider these two seemingly opposed concepts:
- Content length likely isn’t a ranking factor
- Longer content tends to rank higher
SEOs have been debating this for years, and empathetically stress that content doesn’t need to belong to rank. Case in point: Consider this page from the US Government, which ranks for 1000s of searches a month. It doesn’t need extra content because it satisfies the user intent.
On the other hand—all things being equal—longer content tends to rank higher. Nearly every SEO correlation studies ever performed confirm this.
Why? Longer content typically:
- May have a better shot of showing topical relevance
- Has a better chance of containing content that satisfies the user’s query
- Is likely to contain more images and video
- On average, tends to earn more links and shares than shorter content
How to Leverage
In reality, it’s not the length of your content, but the depth of your content that matters. Content that fully explores a topic, including related questions, is likely to earn more visibility that content that only lightly covers a subject.
More: The Google Ranking Factor You Can Influence in an Afternoon [Case Study]
10. Topical Authority
It’s hard—typically—to rank for a competitive search query with only a single page website.
Sites that do well in Google search results tend to publish regularly in specific areas of expertise over time, building content, links, and authority.
We don’t know if Google uses a specific authority metric in its algorithm, but several possible mechanisms may make this concept work:
- Internal Linking
- URL Structure
- Topic clusters
- Author authority
Sites that rank well for a particular topic often find it much easier to rank new content on that same topic, even with few external links.
How to Leverage
- Become an authority on a topic by covering the topic thoroughly over time, creating multiple posts/pages, and earning topically relevant links.
- Organize your topic using smart URL structures, i.e., if you were writing about “link building,” place all your link building post in the /link-building/ folder, so that Google can associate these posts together.
- Build Topic Clusters, leveraging smart internal linking. HubSpot created a great overview of how to accomplish this: https://research.hubspot.com/topic-clusters-seo
11. Structured Data
While Structured Data isn’t an explicit Google ranking factor, it can add content+context to your page to not only help it to rank, but also become more visible in search results.
Structured Data is the content behind your content, and provides search engines with explicit information as to what your content is about.
For example, Product Schema is extremely popular in eCommerce. With Product Schema, you can define aspects of your product such as price, photos, and availability, so that there is absolutely no confusion to search engines. Other popular schemas include:
- Offer
- WebPage / Website
- Rating / Review
- Event
- SearchAction
The SEO agency Distilled has repeatedly shown through testing how adding various types of structured data has helped in rankings. (It doesn’t help in all cases, but often does.)
Aside from adding clarity to your content, the other way Structured Data improves your visibility is by triggering Rich Snippets in search results, which we covered earlier.
How to Leverage
First of all, if you are unfamiliar with Structured Data, how to implement it, or the types of content you should mark up, here are a couple of resources to get you started:
Be sure to test your markup using Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool.
12. Hreflang for Internationalization
If you serve various versions of your website across different countries or languages, hreflang implementation is a must.
Hreflang doesn’t necessarily boost your rankings (though many report that it does exactly this in many situations) but it helps Google to show the right content to the right audience, which can have a profound impact on your search performance.
Check out these case studies, all with search visibility improvements:
- Case Study: The Impact of hreflang Tag
- 3 Hreflang Case Studies
- HREFLang Fix Results in 58% Increase in Local Traffic
Hreflang isn’t appropriate to all circumstances (i.e., you only target web content to a single language and country) but if you want to expand across dialects and borders, it offers a great opportunity.
How to Leverage
Hreflang implementation is straightforward, but the specifics can be daunting even to the most experienced SEO. After you get everything set up, be sure to test using the Sistrix tool below, and checking Google Search Console for hreflang errors.
- Overview: Use hreflang for language and regional URLs
- Generate: The hreflang Tags Generator Tool
- Test: hreflang Validator
13. Volume of Brand Searches
It sounds like a chicken and egg scenario, but it’s actually much more than that: When more people search for your website and/or brand, you tend to show up more frequently in search results.
There are several different ways searchers can search for your brand and associate it with specific keywords:
- Brand: Nike
- Navigational: nike.com
- Brand + Keyword: nike running shoes
- Brand + Navigation: running shoes nike.com
Many marketers have wisely observed that when the volume of these branded searches increases, the brand tends to show up even when searchers aren’t specifically looking for it.
Part of the reason, many SEOs believe, is that brand searches create an entity relationship between the brand and the keyword, i.e., “nike” is an entity associated with “running shoes,” so it tends to show up more when running shoes are searched.
The other reason is much more obvious: brand searches influence Google’s auto-suggest. The more people search for “running shoes nike,” the more likely Google will suggest that exact phrase when people search for “running shoes.”
How to Leverage
Building your brand so that searchers actually seek you out by name (and don’t simply stumble upon you in search results) is one of the strongest drivers of traffic there is. It also helps build a defensive “moat” around your business. The more people looking for your website, the less likely for Google to push down your site in rankings.
Building up your brand is hard work, but there are clever shortcuts many savvy marketers have tried. For example:
- A television commercial that encourages viewers to search Google for “Chicken by Bob” can create branded search around those terms.
- An email campaign that includes a link to a specific Google search containing the brand + the keyword.
14. AMP
Google likes to say that Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) isn’t a ranking factor. And SEOs equally like to point out that AMP is indeed a visibility factor.
The primary advantages that AMP affords are:
- Pages become eligible for Google News Carousels and other features
- Faster load times, which can improve engagement
- Mobile search results are flagged with the AMP symbol, which can increase CTR
For publishers, these advantages can add up quickly. A Google sponsored Forrester study showed a 10% year-over-year increase in traffic and 60% increase in pages per visit for AMP sites.
AMP, despite the advantages, isn’t for everyone. Publishers may find that the technical standards are hard to maintain, and some non-news sites may find that any traffic gains aren’t worth the trouble.
How to Leverage
Setting up AMP can be tricky for smaller sites, but available tools get better each month. Check out these resources:
- Accelerated Mobile Pages Project
- AMP Optimization for Success: SEO Steps, Tips & Tools
- How to Properly Setup Google AMP on Your WordPress Site
15. HTTPS
Even by Google standards, that the actual ranking boost from HTTPS is small. One Googler called it a tiebreaker.
Even so, the SEO benefit from HTTPS is bigger than the sum of its parts.
Part of the reason is the way browsers display HTTPS sites as secure. Currently, most browsers grace secure sites with a trusted green bar, while Chrome aggressively labels certain pages “insecure” if they don’t have HTTPS.
Going forward, browsers may do away with green bars altogether and stated plans to issue warnings for all non-secure pages. In this case, non-HTTPS pages might soon be considered a negative ranking factor by default.
For now, it’s a good idea to implement HTTPS.
How to Leverage
Fortunately, making your site secure through HTTPS is easier than ever. Many web hosts even offer it free through services like Let’s Encrypt and Cloudflare.
Otherwise, we recommend this handy HTTPS migration checklist from Aleyda Solis.